Director : Isabelle MARTY
Keywords
Themes of research
The team "Cellular Myology and Pathologies" gathers basic scientists, geneticists and clinicians, working on muscle pathologies related to defect in muscle calcium release.
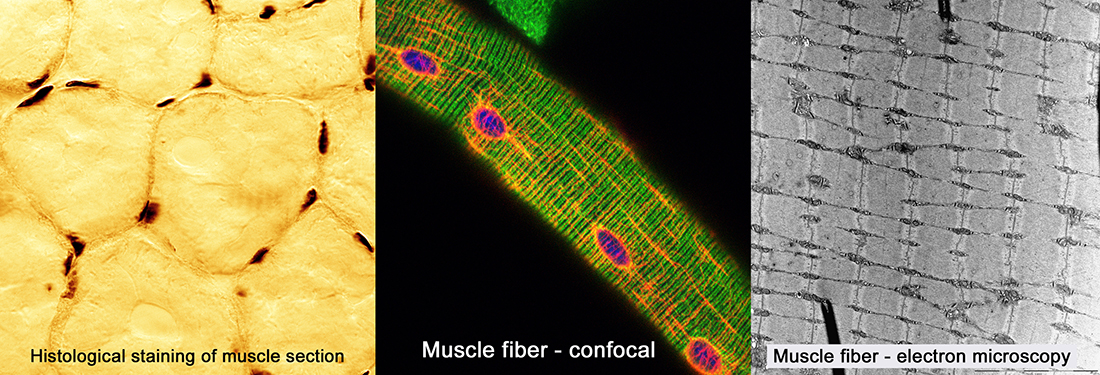
Muscle stimulation at the neuromuscular junction is transformed in a huge intracellular calcium release in a specific part of muscle cell called the triad. This calcium release is performed by a large protein complex, the calcium release complex, specifically localized in the triads. The calcium release complex is organized around RyR1, the calcium release channel, and triadin. Mutations in the calcium release complex proteins (mainly in RyR1) result in a number of rare muscle disease: congenital myopathies (Central Core Disease, Multiminicore Disease), Malignant hyperthermia…. The team "Cellular Myology and Pathologies" gathers basic scientists, geneticists and clinicians, working on muscle pathologies related to defect in muscle calcium release. Understanding the function of this complex, and its targeting to the triad is necessary for the development of new therapies. To reach this purpose, the team develops the following projects:
- Development and characterization of cellular or animal models: understand the function of proteins involved in the complex, and the pathologies related to their alteration.
- Therapeutic development: develop treatments to correct the mutations resulting in congenital myopathies, with a focus on RyRs and triadin mutations.
- Intracellular trafic: study the function of proteins of the calcium release complex in the formation of the complex and in the formation of triads, in interaction with orther elements like microtubules.
Techniques used :
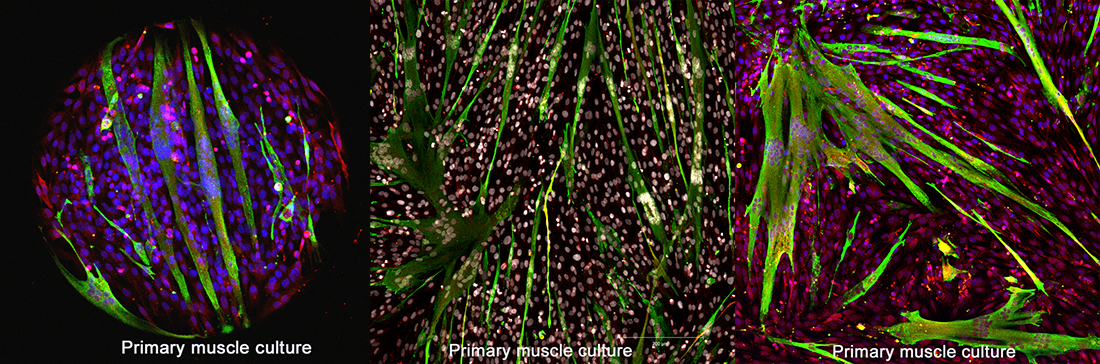
- Molecular and cellular biology: Cloning, RT-q-PCR, transfection, virus production, viral transduction, production and culture of human and mouse muscle cells (primary cultures), in vivo transduction...
-
Biochemistry: Quantitative Western blot, immunofluorescence, immunoprecipitation
-
Confocal microscopy and electron microscopy: Immunostaining, morphological analysis, calcium imaging, FRAP, photoactivation, protein dynamics.
Partners : 
Thesis of the team (in french)
Publications
Oddoux S., Brocard J., Schweitzer A., Szentesi P., Giannesini B., Brocard J., Fauré J., Pernet-Gallay K., Bendahan D., Lunardi J., Csernoch L., Marty I., Triadin deletion induces impaired skeletal muscle function. J Biol Chem. (2009), 284, 34918-34929
Roux-Buisson, N., Cacheux, M., Fourest-Lieuvin, A., Fauconnier, J., Brocard, J., Monnier, N., Ray, P.F., Denjoy, I., Durand, P., Guicheney, P., Kyndt, F., Leenhardt, A., Le Marec, H., Lucet, V., Mabo, P., Probst, V., Lacampagne, A., Fauré, J., Lunardi, J., Marty. I. Absence of Triadin, a Protein of the Calcium Release Complex, is Responsible for Cardiac Arrhythmia with Sudden Death in Human. Hum. Mol. Genet. (2012), 21, 2759-2767.
Fourest-Lieuvin, A., Rendu, J., Osseni, A., Pernet-Gallay, K., Rossi, D., Oddoux S., Brocard, J., Sorrentino, V., Marty, I., Fauré, J. (2012) Role of Triadin in the Organization of Reticulum Membrane at the Muscle Triad, J. Cell Science, 125, 3443-3453.
Rendu J, Brocard J, Denarier E, Monnier N, Pietri-Rouxel F, Beley C, Roux-Buisson N, Gilbert-Dussardier B, Perez MJ, Romero NB, Garcia L, Lunardi J, Fauré J, Fourest-Lieuvin A, Marty I. (2013) Exon skipping as a therapeutic strategy applied to a RyR1 mutation with pseudo-exon inclusion causing a severe core myopathy. Hum Gene Ther. 24,702-713.
Dieterich K, Quijrano-Roy S, Monnier N, Zhou J, Fauré J, Avila Smirnow D, Carlier R, Laroche C, Marcorelles P, Mercier S, Mégarbané A, Odent S, Romero N, Sternberg D, Marty I, Estournet B, Jouk PS, Melki J, Lunardi J. (2013). The neuronal endopeptidase ECEL1 is associated with autosomal recessive distal arthrogryposis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 22, 1483-1492.
Falcone S, Roman W, Hnia K, Gache V, Didier N, Lainé J, Auradé F, Marty I, Nishino I, Charlet-Berguerand N, Romero NB, Marazzi G, Sassoon D, Laporte J, Gomes ER. (2014). N-WASP is required for Amphiphysin-2/BIN1-dependent nuclear positioning and triad organization in skeletal muscle and is involved in the pathophysiology of centronuclear myopathy. EMBO Mol Med. 6, 1455-1475
Marty I. (2015). Triadin regulation of the ryanodine receptor complex. J Physiol. 593, 3261-3266.
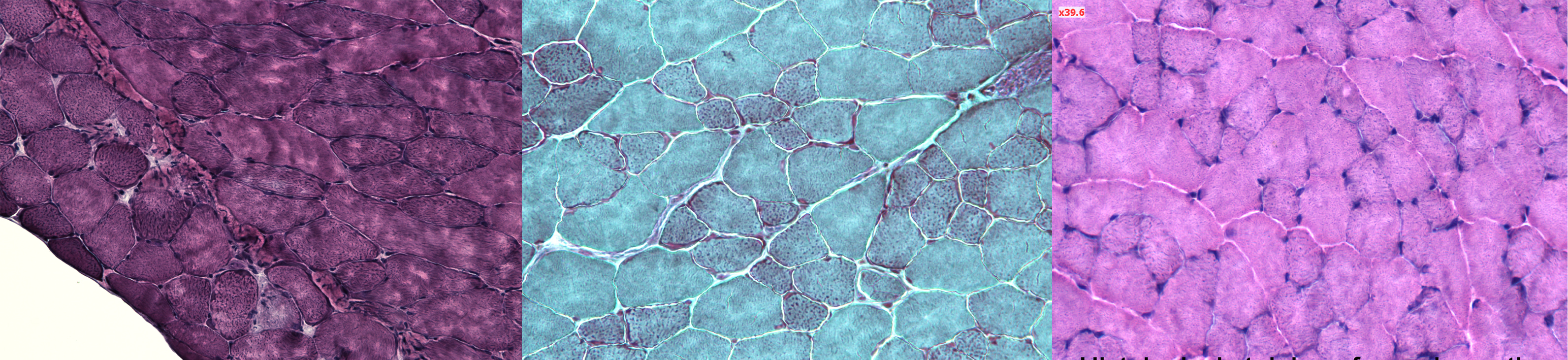
Histological staining of muscle sections
Members
- Mathilde BEAUFILS
- Julie BROCARD
- Alioune FALL
- Julien FAURÉ
- Xénia MARTIN
- MME Isabelle MARTY
- Patrick MERESSE
- Anne-Sophie NICOT
- Anne PETIOT
- Margaret PRAS
- John RENDU
- Robin REYNAUD DULAURIER
- Nathalie ROUX-BUISSON
- Amandine TOUREL