- Share
- Share on Facebook
- Share on X
- Share on LinkedIn
Team F.Saudou
On June 11, 2021
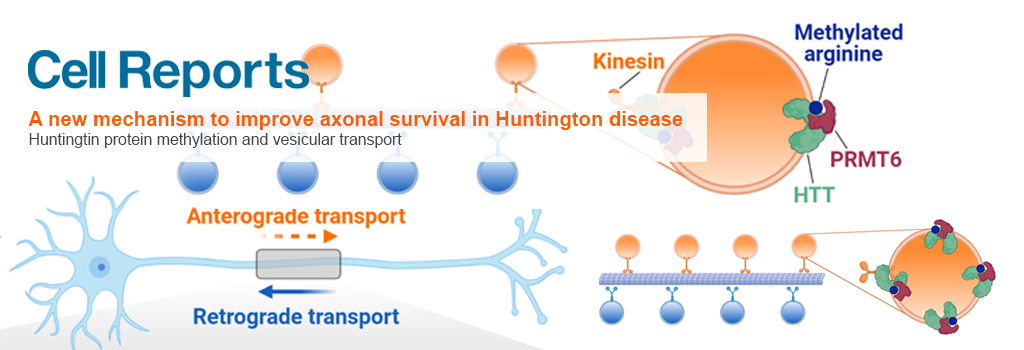
Huntingtin protein methylation and vesicular transport
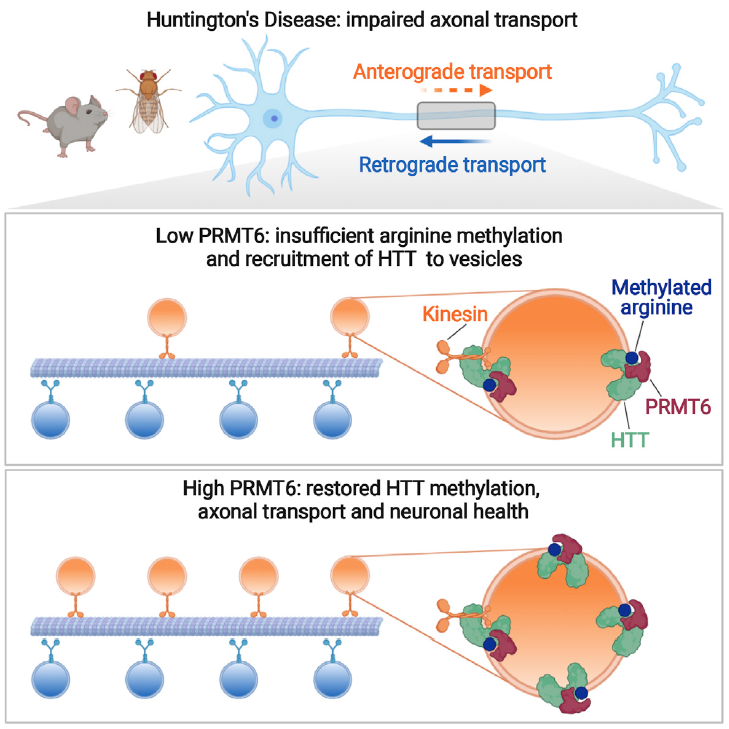
The huntingtin protein (HTT) transports various organelles, including vesicles containing neurotrophic factors, from embryonic development throughout life. To better understand how HTT mediates axonal transport and why this function is disrupted in Huntington’s disease (HD), the Team "Intracellular Dynamics and Neurodegeneration" studied vesicle-associated HTT and found that it is dimethylated at a highly conserved arginine residue (R118) by the protein arginine methyltransferase 6 (PRMT6).
Without R118 methylation, HTT associated less with vesicles, anterograde trafficking was diminished, and neuronal death ensued—very similar to what occurs in HD. Inhibiting PRMT6 in HD cells and neurons exacerbated mutant huntingtin (mHTT) toxicity and impaired axonal trafficking, whereas overexpressing PRMT6 restored axonal transport and neuronal viability, except in the presence of a methylation-defective variant of mHTT.
In HD flies, overexpressing PRMT6 rescued axonal defects and eclosion. Arginine methylation thus regulates HTT-mediated vesicular transport along the axon, and increasing HTT methylation could be of therapeutic interest for HD.
Reference :
Huntingtin-mediated axonal transport requires arginine methylation by PRMT6.
2021, Cell Reports 35, 108980.
Alice Migazzi1#, Chiara Scaramuzzino#, Eric Anderson, Debasmita Tripathy, Ivó H. Hernández, Rogan Grant, Michela Roccuzzo, Laura Tosatto, Amandine Virlogeux, Chiara Zuccato, Andrea Caricasole, Tamara Ratovitski, Christopher A. Ross, Udai Pandey, José J. Lucas, Frédéric Saudou*, Maria Pennuto*, Manuela Basso*
# The authors contributed equally to the work
* Corresponding authors: Manuela Basso (manuela.basso unitn.it (manuela[dot]basso[at]unitn[dot]it)); Maria Pennuto (maria.pennuto
unitn.it (manuela[dot]basso[at]unitn[dot]it)); Maria Pennuto (maria.pennuto unipd.it (maria[dot]pennuto[at]unipd[dot]it)); Frédéric Saudou (frederic.saudou
unipd.it (maria[dot]pennuto[at]unipd[dot]it)); Frédéric Saudou (frederic.saudou inserm.fr (frederic[dot]saudou[at]inserm[dot]fr))
inserm.fr (frederic[dot]saudou[at]inserm[dot]fr))
Date
- Share
- Share on Facebook
- Share on X
- Share on LinkedIn